If you’re building a gaming PC, the CPU can be one of the more intimidating components to choose, especially if you’re new to the world of computer hardware.
Gauging a CPU’s performance isn’t as simple as with GPUs, and all of the numbers and different designations can be quite confusing, to say the least.
So, to make your life a bit easier, this article will explain the Intel Core CPU naming scheme and, hopefully, simplify the task of finding the CPU that best fits your needs!
Table of ContentsShow
Intel Core CPU Naming Scheme
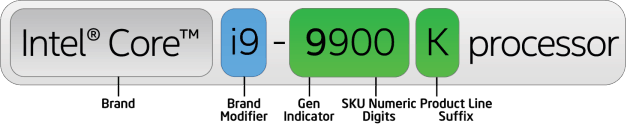
The name of an Intel Core CPU consists of a total of six segments:
- The company name
- The brand name
- The brand modifier
- The generation indicator
- The model number
- The letter designation at the end
Company Name
There’s little to say about the company name — it’s Intel, and it indicates that the CPU has been produced by Intel.
Brand Name
Now, Intel has a number of brands in their CPU selection, all designed for different things. To name the most popular ones that you’ll encounter today:
- Core, aimed mainly at mainstream desktop PCs, be it gaming PCs or workstations.
- Xeon, which includes some of the most powerful CPUs currently on the market with unmatched core and thread counts, intended for heavy-duty workstations and servers.
- Pentium, budget-friendly CPUs that are well suited for casual computer users.
- Celeron, entry-level solutions ideal for those on a tight budget.
- Atom, power-efficient processors mainly designed for mobile devices with limited battery life.
In addition to these five, Intel is also selling Movidius VPUs and Quark microcontrollers. They also had a number of other brands in the past that have since been retired.
Brand Modifier

Intel CPUs are further distinguished according to their overall performance and pricing. When it comes to the Intel Core models, you will find that they are further divided into four categories:
- i3 – The most affordable Core models that are ideal for budget gaming PCs.
- i5 – Mid-range CPUs that are usually the best fit for the average gamer.
- i7 – High-end processors that are great for both gaming and CPU-heavy professional software.
- i9 – Enthusiast-grade CPUs that are usually only really worth buying for workstations.
Generation Indicator

This is another fairly simple part of a CPU’s name, and it indicates what generation the CPU belongs to. The latest Intel desktop CPUs belong to the 12th generation, and that’s what the “12” in “Intel Core i5-12600K” stands for.
Overall, each subsequent CPU generation offers some sort of improvement. Usually, it’s just a general increase in performance but newer generations can also include certain new features that were missing from their predecessors. For example, the 11th generation Core CPUs supported PCIe 4.0, whereas the 10th generation models did not.
Model/SKU Number
The model/SKU number usually consists of 3 digits, and while it is a generic number that doesn’t really say anything about the CPU’s specifications or its capabilities, it does indicate its position in the hierarchy within the generation it belongs to.
For example, you have the i3-10100, the i5-10600, the i7-10700, and the i9-10900, each CPU is more powerful than the last. So, the models designated with higher numbers pack more processing power and may have access to certain features that are missing from the cheaper alternatives.
However, these numbers don’t necessarily mean anything if you’re comparing processors across several generations. That is to say, the cheapest i3 model released this year could easily outperform what used to be a top-of-the-line i7 processor several years ago.
The Letter Designations
Finally, we get to the letter designations, that is, product line suffixes. These are found at the end of the processor’s name, behind the model number, and they usually highlight a certain feature or characteristic that separates that particular CPU from the standard model that comes without a letter designation.
The letter designations that you’ll find in Intel desktop CPUs today are:
- K – The most common designation you’ll encounter if you’re shopping for desktop CPUs. It indicates that the CPU has an unlocked multiplier and can thus be overclocked freely.
- F – Indicates that the CPU lacks the integrated graphics that are usually found in Intel CPUs and thus requires a discrete graphics card. Some models are also marked with KF, meaning that they are both unlocked and lack integrated graphics.
As for mobile CPUs, the common designations that you’ll encounter today are:
- U – Indicates a low-power model with low TDP.
- Y – Indicates an ultra low-power model that features an even lower TDP than the models carrying the U designation.
- T – Indicates yet another low-power model that focuses on power efficiency over performance.
- G1–G7 – Indicates the level of performance you can expect from the CPU’s integrated graphics solution.
- H – Indicates a high-performance CPU. Models marked with an HK indicate that the model is both high-performance and overclockable.
Conclusion
And so, that would be a quick overview of the Intel Core CPU naming scheme and the letter designations that you’ll encounter when shopping for a new CPU today.
We should note that we didn’t include some of the letter designations that were only found in some older, discontinued models, but we’ll keep the article updated in case any of those makes a comeback or if Intel adds some new designations to the mix in the future.
Also, if you’re shopping for a new CPU right now, be sure to check out our selection of the best gaming CPUs of 2023. There you’ll find a more thorough guide and a number of CPUs that might be the perfect fit for your needs.




